Creating and editing a segment
Learn how to create and edit a segment, and define the settings for the segment.
For hands-on examples of creating different types of segments, see Segment examples.
Creating a segment
Before creating a new segment for your site, check whether a similar segment already exists.
To create a segment:
-
In the Frosmo Control Panel, in the sidebar, select Audiences.
-
Click Create segment.
-
To add one or more segmentation rules, click Add new rule, and select a rule type. You can add conditions to and combine the rules to get more specific target audiences.
-
Set the time limit for the segment.
-
Select Description, and enter a descriptive name for your segment. You can also enter a description to better remember what the segment is about.
-
When you're done, click Save.
Editing a segment
To edit a segment:
-
In the Frosmo Control Panel, in the sidebar, select Audiences.
-
In the segments list, find the segment you want to edit, click the quick menu button for the segment, and select Edit.
-
Edit the segment rules and other settings.
-
When you're done, click Save.
Segmentation settings
The basic segmentation settings provided by the Frosmo Control Panel allow you to create effective segments by defining and combining segmentation rules.
Combined segmentation rules are evaluated independently from each other. This means that the visitor doesn't need to match all the rules at the same time, on the same page load, or even within the same session.
For example, if there are two segmentation rules combined and the time limit is set to 14 days, it is enough for the visitor to match both rules during 14 days.
If you need to combine several segmentation rules and need the valuation of them all to happen at the same time, use the trigger segmentation rule.
Segmentation rules
The Control Panel provides the following segmentation rules.
Page view
Segment visitors based on which pages on your site they view or do not view. To do this, you must define:
-
How to identify the viewed page(s)
-
How many page views are required
-
How the page views are counted
You can choose from several URL options depending on how precisely you want to specify the viewed pages:
-
URL: The absolute URL of the viewed page. For example,
http://www.example.com/index.html. -
Protocol: The protocol used in the URL. The possible values are
httpandhttps. -
Domain: The domain name part of the URL. For example, in
http://www.example.com/index.html, the domain iswww.example.com. -
Path: The URL part after the domain pointing to a resource. For example, in
http://www.example.com/index.html, the path is/index.html. -
Anchor: The anchor part of the URL. The anchor is always preceded by the "#" character. For example, in
http://www.example.com/index.html#about, the anchor isabout. -
Query selector: The query string part of the URL. The query string always starts with the "?" character and consists of a key and value separated by the "=" character. For example, in
http://www.example.com/index.html?search=word, the key issearchand the value isword. Using the query selector, you can only define a single key-value pair per rule condition.
You have several options to define how the URL option must match the behavior of the visitor:
-
is exactly
-
is not exactly
-
begins with
-
does not begin with
-
ends with
-
does not end with
-
contains
-
does not contain
-
matches the regular expression
-
does not match the regular expression
You must also define the number of times the visitor must view the specified page(s) in order to get segmented.
Finally, you must define how often a page load is counted as a page view:
-
each page load
-
one page load per session
-
one page load per day
Example
The visitor has viewed a page whose URL is exactly http://frosmo.com/example more than or equal to 3 times, with one page load per day counted as a view.
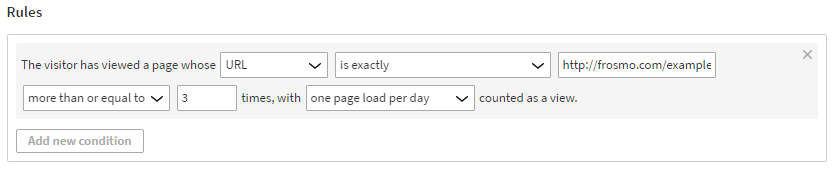
This means that the in order to get segmented, a visitor must view the page with the URL http://frosmo.com/example at least 3 times. Only one page view per day is counted, so the visitor must view the page on 3 separate days.
New visitor
Segment visitors based on whether they have visited your site before. Tracking new visitors is based on sessions; each new session is counted as a new visit and increments the total number of visits. A session ends after 30 minutes of inactivity.
You can define that in order to get segmented, the visitor either is or is not a new visitor on your site.
Site visit
Segment visitors based on how many times they have visited your site. To do this, you must define:
-
How many visits are required
-
How the visits are counted
You can define the number of times the visitor has visited your site.
You must also determine what counts as a visit:
-
each site visit
-
one visit per day
Example
The visitor has visited the site more than or equal to 2 times, with each site visit counted a s visit.
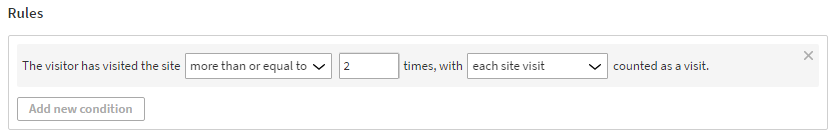
The visitor has visited the site more than or equal to 2 times, with each site visit counted a s visit.
Landing page
Segment visitors based on the first page they view on your site during the current browser session. To do this, you must define:
-
How to identify the landing page(s)
-
How many landing page loads are required
-
How the page loads are counted
You can choose from several URL options depending on how precisely you want to specify the landing page(s). For a list of the options, see Page view.
You have several options to define how the URL option must match the behavior of the visitor. For a list of the options, see Page view.
You must also define the number of times the visitor must land on the specified page(s) in order to get segmented.
Finally, you must define how often a landing page load is counted as a site entry:
-
each site visit
-
one site visit per day
Example
The visitor has entered the site through the domain that contains blog.frosmo.com more than or equal to 1 times, with each site visit counted as an entry.
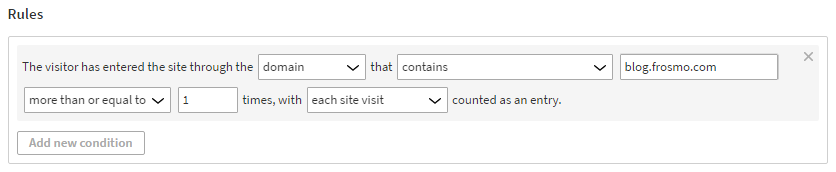
This means that in order to get segmented, the visitor must enter the site through by landing on any page with the domain containing the string blog.frosmo.com (including subdomains) at least once. Each such visit is counted, even if they happen during the same day.
Visit referrer
Segment your visitors based on the page from which they arrive to your site through a link. You must define:
-
How to identify the referrer page(s)
-
How many arrivals are required
-
How the referrals are counted
A page is only perceived as a referrer when the visitor clicks a link on it. Certain sites (such as Google) and links cannot be tracked as referrers.
You can choose from several URL options depending on how precisely you want to specify the referral page(s). For a list of the options, see Page view.
You have several options to define how the URL option must match the behavior of the visitor. For a list of the options, see Page view.
You must also define the number of times the visitor must arrive to the site from the specified page(s) in order to get segmented.
Finally, you must define how often a referral is counted as a site entry:
-
each site visit
-
one site visit per day
Example
The visitor has arrived from a page whose domain contains .frosmo.com more than or equal to 2 times, with one site visit per day counted as a referral.
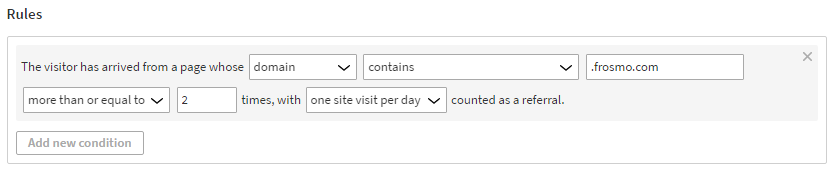
This means that in order to get segmented, the visitor must enter the site through a link from any page with the domain containing .frosmo.com (this includes all subdomains) at least twice. Only one visit per day is counted.
Conversion
Segment your visitors based on the conversions they complete on your site. You must define:
-
Conversion type
-
How many conversions are required
-
How the conversions are counted
Define the type of conversion the visitor must complete in order to get segmented. The default conversion type is "transaction", which means that the visitor purchases a product. For this type of conversion, you also need to define the product(s) .
To use the transaction type of conversions in segmentation, you must have product tracking set up for your site.
Optionally, you can create custom conversion definitions to track conversions related to other visitor actions, such as button clicks, registrations, or triggers.
You must also define the number of times the visitor must complete the conversion in order to get segmented. If there are more than one selected products and/or more than one conversions are required in order for the visitor to get segmented, both products must be included in each conversion.
Finally, you must define how often completing the conversion is counted as a conversion:
-
each conversion
-
one conversion per visit
-
one conversion per day
Example
The visitor has completed the transaction conversion with 1 selected product(s) more than or equal to 1 times, with each conversion counted.
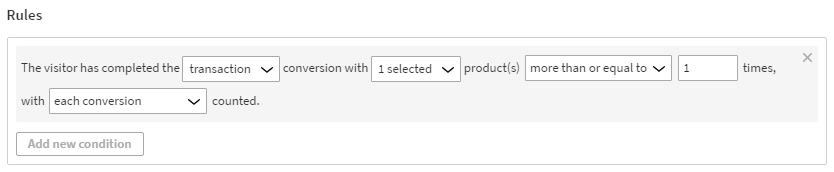
This means that in order to get segmented, the visitor must complete a transaction by purchasing the specified product at least once. Each conversion is counted, even if there are more than one in a day.
Custom action
Segment your visitors based on whether they complete a specific custom action with predefined values. You must define:
-
Custom action type
-
Values with which the user must complete the event
-
How many events are required
-
How the events are counted
You can only use custom actions in segmentation if there are custom actions created for your site.
Product view
Segment your visitors based on which products they view in a selected product category. You must define:
-
Product category and products
-
How many product views are required
-
How the product views are counted
To select a product category and products, you must have product tracking set up for your site.
You must define the product category and products. You can select several products in the given product category. The visitor gets segmented if they view any of the selected products, that is, if the product page is loaded.
When you set up the initial product tracking or create new product categories for the site, it takes up to 24h for the product categories to be available for segmentation.
You must also define the number of times the visitor must view the specific product(s) in order to get segmented.
Finally, you must define how often a product page load is counted as a view for that product:
-
each page load
-
one page load per visit
-
one page load per day
Example
In the animals product category, the visitor has viewed 1 selected product(s) more than or equal to 3 times, with each page load counted as a view.
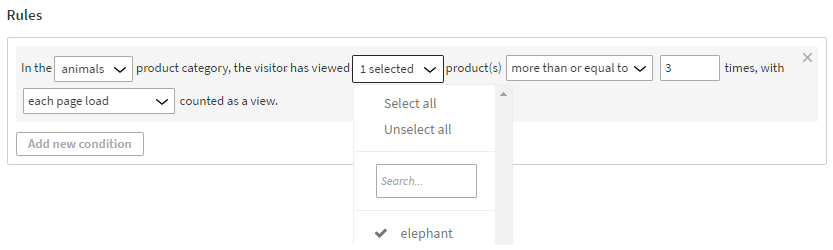
This means that in order to get segmented, the visitor must view the selected animal in the animals product category at least 3 times. Each animal page load is counted as a product view, even if they happen during the same visit or day.
To select all products in the selected product category, keep the default value (any) in the product field. To select all products in the drop-down product list, click Select all. To filter the products, start writing the product name in the search field.
Product purchase
Segment your visitors based on the products they purchase on your site. You must define:
-
How many purchases are required
-
Purchased products
To select products, you must have product tracking set up for your site.
You must define the number of times the visitor must purchase the specified product(s) in order to get segmented.
Example
The visitor has purchased less than or equal to 3 of elephant product(s).
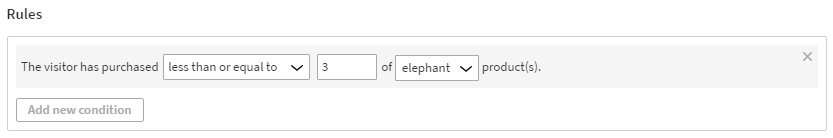
This means that in order to get segmented, the visitor must purchase at least one, but no more than 3, elephants.
Trigger
Segment your visitors based on trigger event. You must first create relevant triggers in the Control Panel to use them in segmentation. You must define:
-
Trigger
-
How the trigger events are counted
You must select the trigger and define the number of times the visitor must fire the trigger in order to get segmented.
Finally, you must define how often the trigger event is counted for segmentation:
-
each trigger event
-
one trigger event per visit
-
one trigger event per day
Example
The visitor has triggered Cheetah button click more than 1 times, with one trigger event per session counted.
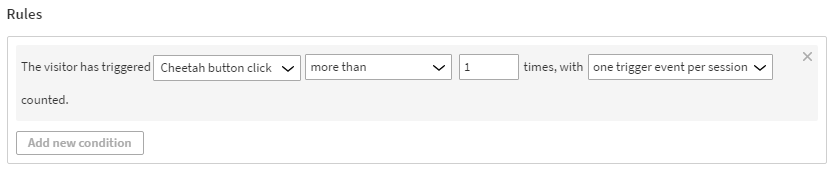
This means that in order to get segmented, the visitor must click a specific button more than once. Only one click per visit is counted.
Combining segmentation rules
You can combine segmentation rules by adding "AND" and "OR" conditions. To add a condition to a rule, click Add new condition . There is really no difference between a rule and condition; they are just separated to enable creating more complex segments.
Combining two segmentation rules with the "AND" condition means that in order to get segmented, a visitor must match both rules. The "OR" rule means that in order to get segmented, the visitor must match at least one of the rules but not necessarily both
Example
In the animals product category, the visitor has viewed 1 selected product(s) more than or equal to 3 times, with each page load counted as a view.
AND
The visitor has arrived from a page whose URL is exactly http://www.frosmo.com more than or equal to 1 times, with each site visit counted as a referral.
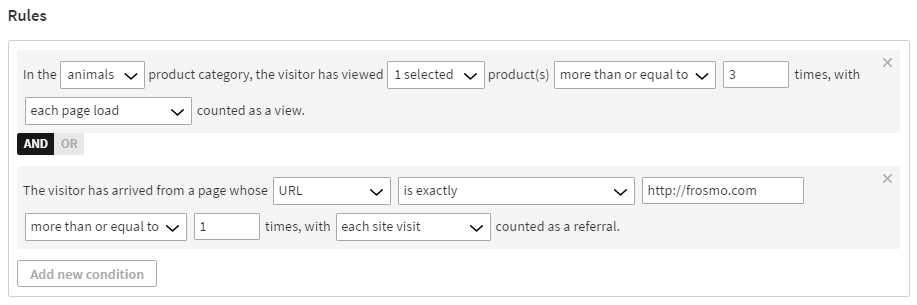
This means that in order to get segmented, the visitor must view the selected animal in the animals product category at least three times, and the visitor must also arrive to your site from the http://www.frosmo.com page at least once.
You can create more complicated segments by combining multiple rules. To add another rule, click Add new rule.
Example
The visitor is a new visitor.
AND
(
The visitor has entered the site through the URL that is exactly http://www.frosmo.com more than or equal to 1 times, with each site visit counted as an entry.
OR
The visitor has arrived from a page whose URL begins with http://example.com more than equal to 1 times, with each site visit counted as a referral.
)
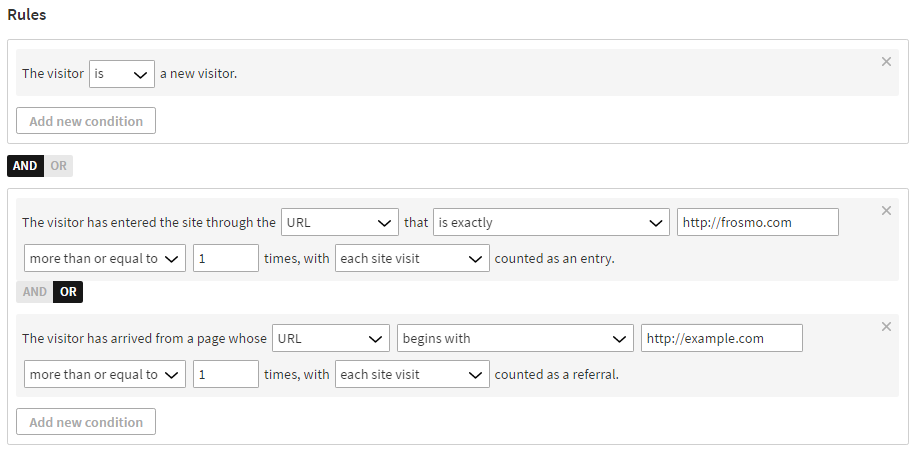
This means that new visitors on the site are further segmented based on whether they enter the site through the www.frosmo.com landing page or come from the example.com website. Visitors who enter the site through other URLs or sites are not segmented.
You can also combine segments using segment groups.
You can create as many and as complicated segments as you like. However, carefully think about what your goal is regarding your target audience to plan relevant segment combinations.
Time limit
The time limit defines the period of time within which a visitor must perform the actions defined in the segmentation rules in order to get segmented. The rules and time limit are evaluated on every page load, which means that a visitor is removed from the segment as soon as the time limit has passed and in case the rules no longer apply to them.
For example, if the segmentation rule defines that to get segmented, the visitor must visit a specific page on your site at least two times, and the time limit is set to 5 days, segmentation only happens if the visitor visits the page at least two times within 5 days.
If the visitor visits the page once on day 1 and once on day 2, they are segmented. On day 6 the visitor drops out from the segment unless they have visited the page again after day 2.
If the segmentation requires several actions (for example, A and B), the time is counted from the moment the visitor takes either one of these actions. This means that if the time limit is set to 14 days, and the visitor takes action A today, they must take action A again within 14 days in order to stay in the segment regardless of when they take action B.
The default time limit is 14 days.